Forschungsberichte
Wissenschaftliche Veröffentlichungen
Hier finden Sie Veröffentlichungen mit Bezug zu den Forschungen des i-LUM Projekts.
Methodik zur ganzheitlichen Analyse bodengebundener Infrastruktur für Urban Air Mobility
Eltgen, J.; Fraske, T.; Mavraj, G.; Swaid, M.; Kloock-Schreiber, D.; Röntgen, O.; Schüppstuhl, T.
Abstract
Dieser Artikel stellt den methodischen Prozess einer Szenarienentwicklung sowie einer simulationsgestützten Analyse für die bodengebundene Infrastruktur von UAM dar. Als innovative Lösung verspricht UAM im Personentransport Angebote im Gesamtverkehr zu schaffen, um das zukünftige Mobilitätsangebot in Metropolregionen zu verbessern. Die Gestaltung der Nachfrageszenarien befindet sich in einer stetigen Aushandlung zwischen den Akteuren und wird beeinflusst von der technischen Entwicklung, der sozioökonomischen Realisierbarkeit und den zugrunde liegenden Diskursen, die diese Form der Mobilität umgeben. Die Anforderungen an die bodengebundene Infrastruktur sind essentiell für eine realistische Beurteilung der Kapazitäten und Flugmissionen, der städteplanerischen und architektonischen Umsetzung, den Synergien zu anderen Verkehrssystemen sowie einer Berücksichtigung sozialer Aspekte in der Stadt. Der erste methodische Baustein beleuchtet den kreativen Prozess dieser Szenarienentwicklung, einschließlich einer Faktorenanalyse, der Ableitung schlüssiger Nachfrageszenarien sowie der Identifizierung konkreter Standorte für Vertiports am Beispiel der Metropolregion Hamburg. Vier thematische Szenarien werden in diesem Kontext tiefergehend diskutiert: die Anbindung peripherer Räume, Pendlerbewegungen, touristische Nutzung sowie die Überwindung von Mobilitätsengpässen. Im zweiten Abschnitt liegt der Fokus auf der technischen Umsetzung und Analyse der Topologien, Wartungs- und Reparatursystemen, dem Energiemanagement sowie der Wechselwirkung zwischen diesen Subsystemen.
Keywords: UAM, VTOLs, Szenarienentwicklung, Zukunftsrobustheit, Infrastruktur, Topologien, MRO, Energiemanagement, Vertiport
DLRK Deutscher Luft- und Raumfahrtkongress 2023
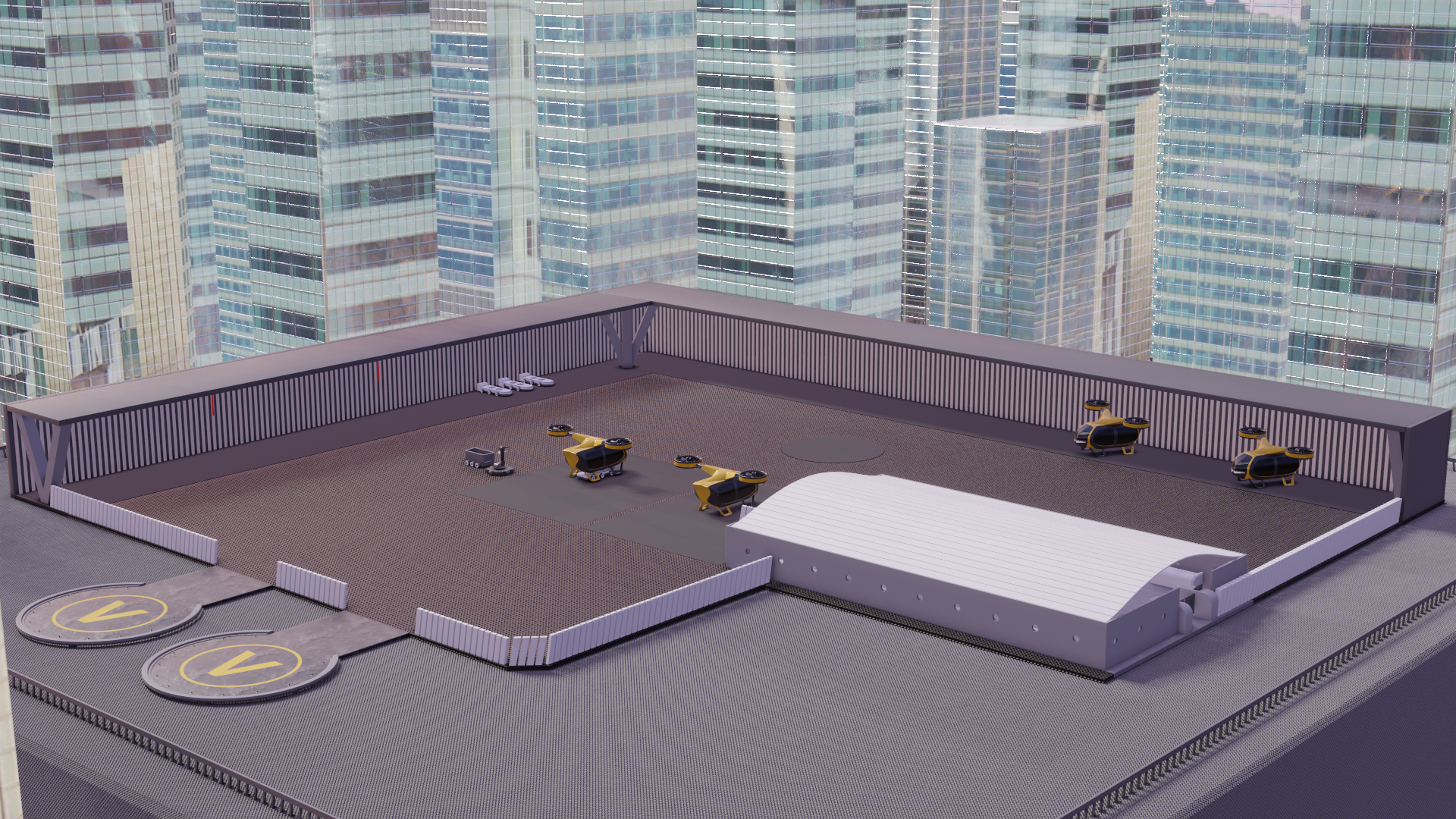
MROPort for Airworthiness Checks of VTOLs in a Future-Proof Environment
Eltgen, J.; Schüppstuhl, T.
Abstract
In this paper, we conduct, how maintenance and repair aspects will affect future-proof operation perspectives from scenario definition and analysis, and how they can be implemented effectively in the holistic system of GBI for the AAM. Therefore, techniques were analyzed and evolved to ensure airworthiness, operation management, and robust modeling. Hence, we can derive MRO capacities. Therefore, we model the MRO aspects in the RCE tool MROPort. This tool depicts maintenance schedules, downtimes, and intervals. The downtimes are deciding to manage the whole operating system in the holistic system of the AAM. More holistic systems for the MRO will be created with the found boundary conditions of VTOLs and GBI. Furthermore, the space needed for the MROPort will be calculated. With urban management analysis, MROPort placement strategies and MRO downtimes result.
AIAA Aviation 2023
Schall und Rauch: Lärmsteuerung im urbanen Verkehr der Zukunft
Johannsen, Josina
Abstract
Der Tagungsband dokumentiert die Vorträge, die auf dem JuWissDay 2022 in Hamburg gehalten wurden. Die Beiträge nehmen die Notwendigkeit größerer Klimaschutzambitionen für Städte in den Blick und verbinden zwei dynamische Regelungsfelder: die Technikentwicklung mit der zunehmenden Autonomisierung technischer Komponenten und das Umwelt-, Klima(schutz-) und Nachhaltigkeitsrecht. Aktuelle Entwicklungen mit einem Fokus auf Städte werden in den Referenzgebieten des Energie-, Bau-, Fachplanungs-, Verkehrs- und Infrastrukturrecht ebenso betrachtet wie grundlegende Fragen zu Klimaschutz und Innovationen. Mit Beiträgen von Dr. Svenja Behrendt | Antonia Boehl | Jakob Feldkamp | Charlotte Heppner, LL.B. | Josina Johannsen, LL.B. | Judith Kärn | Dr. Michael von Landenberg-Roberg, LL.M. (Cambridge) | Emanuele Leonetti | Julian Senders | Tim Schilderoth | Prof. Dr. Sabine Schlacke | Dipl.-Jur. Katja Schubel, B.A. | Prof. Dr. Dana-Sophia Valentiner | Swen Kühn, LL.B.
in: Klimaschutz und Städte: Herausforderungen und Potentiale des öffentlichen Rechts – Tagungsband zum JuWissDay 2022, herausgegeben von Prof. Dr. Dana-Sophia Valentiner, Nomos, Baden-Baden 2023 (open access), S. 189-210.



Analyse von Energieverbrauchsmodellen für elektrisch betriebene Transportdrohnen
Mavraj, G.; Fu, Y.; Avdevičius, E.; Schulz, D.
Abstract
Der Energieverbrauch ist eine entscheidende Einschränkung für den elektrischen Betrieb von Transportdrohnen. Der vorliegende Artikel stellt eine Übersicht verschiedener Drohnen-Energieverbrauchsmodelle unter Verwendung einheitlicher Notation dar. Hierbei werden relevante Einflussfaktoren und deren Wechselwirkung mit der Konfiguration der Drohne analysiert. Die Modellergebnisse werden hinsichtlich dem Energieverbrauch pro Meter (Epm) derselben Drohnenkonfiguration während einer stationären Flugphase analysiert.
Hamburger Beiträge zum technischen Klimaschutz – Analyse, Digitalisierung und Flexibilisierung von Energiemärkten, Elektromobilität, Sektorenkopplung, Elektroenergienetzen und Wasserstoffsystemen
A Systematic Review of Ground-Based Infrastructure for the Innovative Urban Air Mobility
Gazmend Mavraj, Jil Eltgen, Tim Fraske, Majed Swaid, Jan Berling, Ole Röntgen, Yuzhuo Fu, Detlef Schulz
Abstract
the increasing level of urbanisation and traffic congestion promotes the concept of urban air mobility (UAM), which has become a thriving topic in engineering and neighbouring disciplines. the development of a suitable ground-based infrastructure is necessary to supply these innovative vehicles, which mainly includes networks of take-off and landing sites, facilities for maintenance, energy supply, and navigation and communication capabilities. Further requirements comprise robust business and operating models for emerging service providers and regulatory frameworks, particularly regarding safety, liability and noise emissions. the objective of this study is to provide an overview of the current results and developments in the field of UAM ground-based infrastructure by conducting a systematic literature review (SLr) and to identify the most relevant research gaps in the field. For the systematic literature analysis, our search string contains vertiports and the equivalents, UAM and equivalents, and search phrases for the individual domains. In the final analysis 64 articles were included, finding a strong focus on simulations and vertiport networks, while specific case studies and related aspects like automated MrO and urban planning appear less frequently. therefore, this article provides insights for a more holistic perspective on challenges and necessities of future UAM.
Transactions on Aerospace Research, vol.2022, no.4, 2022, pp.1-17
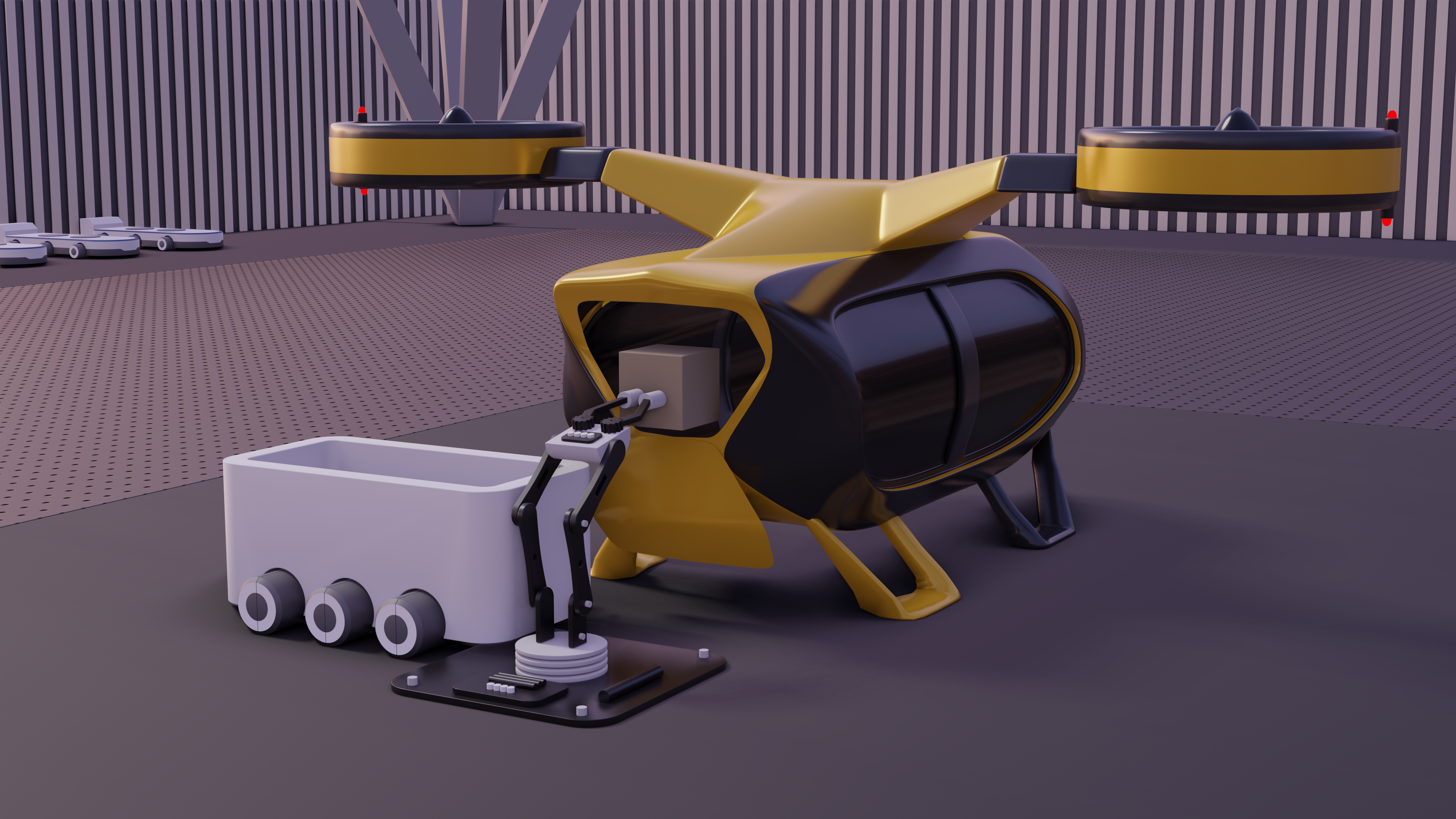

Technical Concepts for Inspecting UAVs for Damage
Jil Eltgen, Thorsten Schüppstuhl
Abstract
The current movement toward urban air mobility (UAM) shows the importance of a ground-basedinfrastructure network to provide urban air vehicles (UAV). To ensure the safety aspect it is necessary to developa system that can inspect the arrived UAV for damages. Therefore, technical concepts for inspecting UAVs fordamage are elaborated. To identify the best system for technical development under the presented conceptsevaluation criteria must be defined and applied. These include properties, technical systems, and other criteriasuch as the costs. In the first step for every UAV inspection system, the differences between the motionsequences will be examined. In the second step, there will be an investigation of the sensor systems presented.In conclusion, the systems with the best results in both parts are merged for an inspection setup for furtherinvestigations.
Proceedings of the 33th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences Stockholm, Sweden
Verwaltungsrechtliche Fragen des unbemannten Luftverkehrs – Herausforderungen der U-Space-Verordnung für das nationale Recht
Christian Worpenberg, Dr. Dana-Sophia Valentiner, Josina Johannsen, Dr. Katharina Goldberg
Abstract
Der Beitrag beschäftigt sich mit den aktuellen Entwicklungen im Recht der unbemannten Luftfahrt. Nach dem Erlass der Durchführungsverordnung (EU) der Kommission 2021/664 über einen Rechtsrahmen für den U-Space vom 22.4.2021 (im Folgenden: U-Space-VO) stellt sich die Frage, welche Auswirkungen die Verordnung auf das nationale Luftrecht hat. Ziel des Beitrags ist es, nach einer kurzen Aufarbeitung des neuen regulatorischen Rahmens Anpassungsbedarfe des geltenden Luftrechts in Deutschland, insbesondere im Spannungsfeld von hoheitlicher Aufgabenwahrnehmung und Wettbewerb, zu identifizieren und Gestaltungsmöglichkeiten und -herausforderungen, etwa im Zusammenhang mit der Beleihung, auszuloten.
Neue Zeitschrift für Verwaltungsrecht (NVwZ) 2022, S. 1182 = NVwZ-Extra 10/2022, S. 1-9